Abstract
This present study was carried out to assess the prevalence of
brucellosis and blue tongue in a trans humane sheep flock of
Tamil Nadu, India. This Sheep flock had a history of inconsistent
abortion, repeat breeder, poor fertility rate and higher prevalence
of still birth. Serum samples were collected from sheep by random
sampling. Serum samples were subjected to Rose Bengal Plate
agglutination test (RBT) and ELISA. The risk factors like pregnancy,
abortion, age and sex were correlated to the Brucella seropositivity.
This study also assessed for the presence of Bluetongue in aborted
sheep. It was found that ELISA could be the choice of test for
testing of Brucellosis (with the percentage of 57.14). Clinically
healthy rams were found to be with brucellosis seropositivity and
posed infertility to ewes. It was observed that in trans humane flocks.
Brucellosis and Blue tongue has a confounding phenomenon
for ovine abortions.
Keywords: Sheep; Trans Humane; Inconsistent Abortion; Brucellosis; Blue Tongue; Confounding
Introduction
Brucellosis is a bacterial zoonosis caused by microorganisms
belonging to Brucella, a genus of gram-negative bacteria that
behave as facultative intracellular pathogens of ruminants, suidae,
canids, and several wildlife species (OIE, 2008). B melitensis is the
foremost etiological agent of brucellosis in sheep and goats. It is also
the main agent responsible for human brucellosis known as Malta
fever. Abortion and infertility are the predominant clinical signs
in small ruminants. B. melitensis infection in sheep and goats has
been neglected for long time, because small ruminant production
was considered as a represents generally low-income activity
practiced by landless farmers and marginalized communities in the
developing countries. For these reasons the trans humane farming
systems continue to have served disease challenges and pose
major hurdles in, the control and eradication of many infections.
The reasons for such high prevalence may also be result of socio
cultural factors, which were compounded by the lack of adequate
control measures being applied in small ruminant production
systems as per the observations of WHO [1]. The Rose Bengal
Plate Agglutinations Test (RBT) was developed originally for the
diagnosis of bovine brucellosis and despite a scant information on
its usage for Sheep and Goat is available, it is also recommended for
the screening of B. melitensis infection in small ruminants [2]. In
general, indirect ELISA was considered good test for surveillance
purposes in which vaccination is no longer used [3]. Infected nonpregnant
livestock may not demonstrate clinical signs of infection
and this makes the control and prevention more challenging [4].
Bluetongue, which is caused by the Bluetongue virus (BTV) and
transmitted by Culicoides spp. Midges, is a major infectious disease
of sheep [5,6]. Among the economic losses resulting from BTV
infection are abortion and those due to congenital deformities such
as hydranencephaly and cerebellar aplasia in calves and lambs [7].
BTV serotypes -10, 11, 13 and 17 are able to cross the placenta
and cause fetal infection [8]. Limited information on concurrent Brucellosis and Blue tongue in Sheep, especially trans humane
flocks are available. This study investigated and documented it in a
trans humane Sheep flock of Tamil Nadu.
Materials and Methods
Study Area and Flock Details
This study was carried out during the period between
November 2015 to November 2016 in the Cavery delta districts of
Tamil nadu, India. These delta districts are the rice bowl of Tamil
nadu state and accounts for 75% of the state’s rice production. The
rice harvesting season attracts the several Sheep shepherds to this
area to graze the paddy fields after harvesting. Trans humane sheep
flocks having flock strength ranging from 300 to 5000 animals per
ownership are common sights in these areas. Each flock may have
about 300 sheep 25 goat and 9 cattle (Figure 1). These animals
were not immunized against brucellosis and blue tongue and no
periodical deworming programs are followed. In fact no organized
animal health care is being practiced by such nomadic farmers.
Figure 1: Trans human Sheep flock with shepherd in delta
districts of Tamilnadu.

Choice of Samples
Samples were collected from pregnant non aborted, pregnant
aborted, non pregnant ewes and rams. For sample size calculation,
expected prevalence of brucellosis was assumed as 20 percent with
five percent absolute frequency.
Sampling Methods
Clinical materials like whole blood in EDTA tubes, serum
collected in clot activator tubes aseptically and stored in
refrigeration until further processing. Simple random sampling
method was used for sampling.
Brucellosis Screening
Clinical samples like serum samples were collected and
submitted for Brucellosis, Blue tongue, Chalymidiasis, Malignant
catarrahal fever and Bovine viral diarrhoea diseases since the
season and clinical history had given clues for such pathogens. Rose
Bengal plate agglutination test (RBT) and I ELISA tests undertaken
for brucellosis identification.
Blue Tongue Screening
For blue tongue identification, whole blood in EDTA was
collected and subjected to polymerase chain reaction.
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea (BVD) Malignant Cattarhal Fever
(MCF) and Chalymidiasis Screening
Serum samples were collected aseptically and analyzed
by nested PCR for BVD and MCF. Serology was carried out for
Chalymidiasis.
Test Protocols
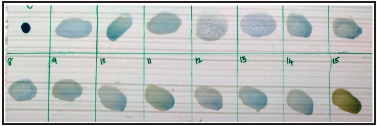
Rose Bengal plate agglutination (RBT) was carried out as
per the OIE prescribed procedure. The recommended steps to
improve sensitivity of RBT by using three volumes of serum and
one volume of antigen (e.g. 75μl and 25μl, respectively) in place
of an equal volume of each (Figure 2) This was used in this study
modification helped in increasing RBT sensitivity and minimized
the discrepancies between RBT and other diagnostic tests. Positive
serum and antigen purchased from Indian Veterinary Research
Institute (IVRI), Bareilly, India was used in this study. Monoclonal
based blocking ELISA for diagnosis of brucellosis was adopted as
per the manufactures protocol. For Blue tongue Polymerase chain
reaction was adopted as per the standard procedure of OIE.
Figure 2: Modified Rose Bengal plate Agglutination Test.
Results
The trans humane sheep population had a clinical history
of inconsistent abortion, pooer birth weight of lambs and higher
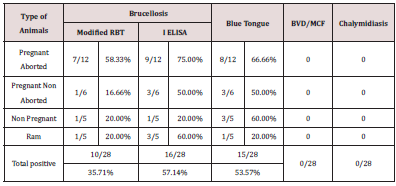
mortality among lambs. Upon screening of 28 clinical samples 15
samples were confirmed as blue tongue with percentage positivity
of 53.57. For Brucellosis, out of 10 (35.71%) animals tested by
RBT and 16 animals tested by I ELISA (57.14%) were positive for
Brucellosis. Out of 12 pregnant aborted animals studied 8 (66.66%)
were positive for blue tongue and 7 (58.33%) were shown positive
for brucellosis (Table 1) In pregnant non aborted animals, out of the
six animals studied three were positive for blue tongue and none of
these were positive for brucellosis. Out of five bucks screened, one
was positive for blue tongue and two were positive for brucellosis.
In non pregnant non aborted animals three and one animals were
positive for blue tongue and brucellosis respectively (Table 2).
None of the animals were positive for malignant catarrhal fever,
Chalymidiasis and Bovine viral diarrhea.
Table 1: Comparison of RBT with ELISA.

Table 2: Comparison of RBT with ELISA.
Discussion
Brucellosis and its mode of transmission were known for
over 100 years still, the disease remains inconsistent pandemic,
predominantly in developing countries. This study analyzed the
cause for in consistent abortion in trans- humane sheep flocks
of delta regions of Tamil nadu, India. These sheep flocks were
nomadic in nature and following flock matting system. They used
to exchange their breeding rams with each other over the period
of time. The results of the study indicated that 53.57 % of animals
were positive for blue tongue and 57.14% were having antibodies
for brucellosis which underscored that the incidence was quiet high.
Many previous studies had documented it and had an increasing
trend [9,10]. The results from this study indicated that brucella
antibodies are widely distributed throughout the flock. Since the
flock was not immunized in their life time, presence of antibodies
directly correlated to the active infection. Prevalence seems to be
higher than the overall country seropositivity (13.5%) in Sheep
[11-13]. Indirect ELISA showed higher positivity (57.14%) than
RBT (35.71%) which indirectly revealed the sensitivity of these
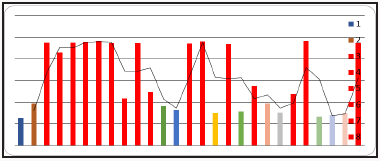
tests (Table 3). More over Monoclonal based blocking ELISA for
brucellosis detects the antibodies with traces and LPS coated on
the ELISA plate has highly homology of the field variant and showed
higher titer value (Figures 2 & 3) Conventional Rose Bengal plate
agglutination test detects only IgM and is less sensitive, where as
ELISA detects both IgM and IgG antibodies which attracts higher
sensitivity [2]. Inconsistent abortion was recorded in this flock
indicated that it could be the “chronic Brucellosis form”. Rams
played vital roles in the transmission of Brucellosis here since
higher number (60%) of them showed seropositivity for brucellosis.
Table 3: Categorization of screening tests and positive for Brucellosis and Blue tongue.
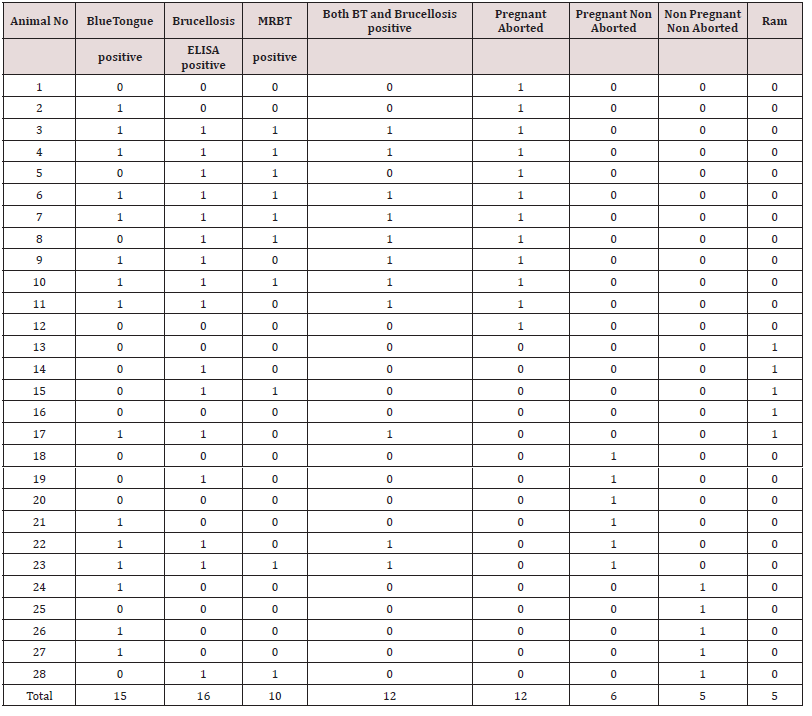
Figure 3: Higher Brucella IELISA titre of Sheep samples.
In India mostly the sero positive animals were handled based
on “test and separate” policy rather than the “test and slaughter”
policy due to economic concerns of these marginalized nomadic
people. Unplanned immunization program coupled with no effective
quarantine and uncontrolled trans-state migration of animals are
major factors that affects the Brucellosis control programs [9]. Host
susceptibility is also variable with the reproductive status. Thus in
the field level, all intermediate stages between typical acute infection
to complete resistance may be observed. Under pregnant aborted
animals category 58.3% and 66.66% animals showed positivity for
Brucellosis and Bluetongue respectively and this highlighted that
there is certain confounding effect which makes the animal to abort.
In pregnant non aborted category lower percentage of animals
showed positive for both Brucellosis and Bluetongue which further
supports the possibilities of confounding phenomenon augmenting
abortion feature. Interesting by aborted animals got pregnant in
their next season and gave birth to normal lambs possibly many
animals may develop self limiting infections or they become
asymptomatic latent carriers and turn in to potential source of
future infections. Abortion generally does not occur if the female is
infected at the last stage of pregnancy. Non pregnant non aborted
animals showed higher Blue tongue positivity than brucellosis
which enlightenend the real risk factor for abortion. Non-pregnant
animals exposed to small numbers of organisms may develop selflimiting,
immunizing infections or they may become latent carriers
[12,13]. No proper selection of breeding ram between flocks of
Sheep, low /no biosecurity measures, poor awareness about the
vaccination had resulted in brucellosis becoming a continuous
threat to the trans humane Sheep populations. As 60 % of rams,
showed seropositivity for brucellosis, they posed a great threat to
the breeding ewes. Interestingly non of the rams showed clinical
signs of Brucellosis. Asymptomatically infected rams deserve to
have poor fertility and contributes to dissemination of B. ovis and
when very high percentage of rams were infected marked infertility
becomes evident in the flock [14]. Seroconversion and shedding of
bacteria in the semen of infected rams demonstrated mild or no
detectable lesions during the acute phase of infection [15].
The study period of October month had a higher culicids’
populations and it in turn would have helped in transmission of
Blue tongue. Results here indicated that BTV is epidemiologically
important, and further studies are required to determine the true
spatial distribution and cause for abortion in Sheep. Unplanned and
uncontrolled grazing and frequent addition of flocks of sheep also
contribute to the wide distribution of brucellosis in these animals.
Even though the goat and cattle reared along with sheep flock, they
were not part of this study, however they may had also acted as a
cofounder for Brucellosis. Future studies on these aspects will add
more information.









